Enterprise Risk Management

Fostering a strong risk-aware culture
JG Summit continues to strengthen its enterprise risk management (ERM) practices to support business growth and long-term sustainability. With the increasing volatility and complexity in the global and national landscape, we continuously refine our risk management processes to deepen our understanding of key business risks and enhance the organization’s capabilities in proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Our risk management approach is guided by the principles outlined in the COSO ERM Framework, connecting strategy setting with governance and risk management processes to foster a strong risk-aware culture across the organization. We have also integrated sustainability and climate-related risks and opportunities into the Company’s ERM framework, aligning our risk strategies with long-term ESG considerations to ensure a holistic approach in addressing key business risks.
In line with this commitment, we conducted several ERM capability-building initiatives across different levels of the organization during the year. These programs include risk assessment methodology training for risk owners and custodians, and risk learning sessions for the general employee population to promote first-line risk awareness and risk management behaviors. Our annual group-wide CRO conference also continually enriches our CROs and risk leaders with knowledge on ERM best practices, evolving issues, and emerging risks.

ERM teams across the group participate in climate risk assessment simulation during the 2024 Gokongwei Group CRO Conference

Risk owners and custodians attend a Bow-Tie Methodology workshop
Risk Management Process
At the parent level, the Company provides guidance on the ERM framework to promote alignment in the risk management approach across the Group. It also fosters group-wide sharing of best practices and ERM learning initiatives. Each SBU establishes its own risk governance structure and processes to address the unique risks of its operations, according to its business environment, risk profile and strategic and operational goals.
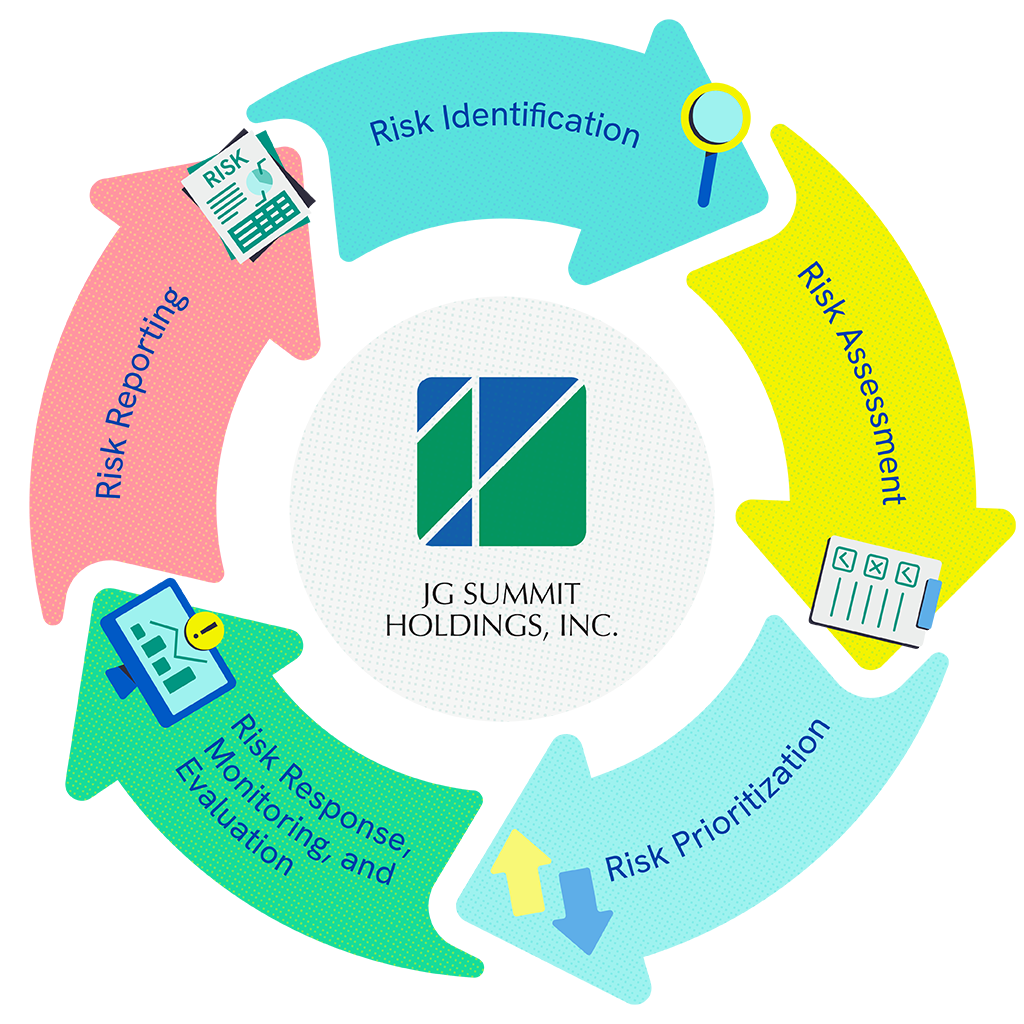
Risk Identification, Assessment, and Prioritization
Risks are identified using different tools such as risk factor analysis, megatrends analysis, and systems dynamics analysis. Identified risks are categorized, and their potential impact is evaluated based on the risk assessment scale we developed for various impact areas. Likewise, we set the likelihood parameters to define the probability of occurrence of the risks. Each operating company develops its own risk assessment scale according to its context and risk appetite.
Highly-rated risks are subjected to further evaluation for prioritization, considering the organization’s overall risk profile, level of vulnerability, and contribution to amplifying certain risks. Furthermore, we also consider the urgency of the risks, which is a factor of velocity or how quickly we will feel the impact of the risks when they materialize, and mitigation timeframe or the length of time needed to manage these risks.
Strategic Risk
Concerns events that could affect the outcome of strategic decisions, such as mergers and acquisitions, key investments, resource allocations, and new business ventures.

Reputational Risk
Refers to anything that could impact the company’s brand value, public perception and stakeholder relationships.

Governance Risk
Pertains to risks related to implementating and adhering to policies and procedures and ethical practices within the organization.

Emerging Risk
Refers to new or developing risks that the company has little to no experience in.

Climate Risk
Refers to potential physical risks that may arise from climatic events or business risks arising from regulatory efforts or changing stakeholder expectations associated with the shift towards a carbon-neutral economy.

Operational Risk
Relates to factors that could disrupt routine business activities or impair property, infrastructure, and security.
IT and Digitalization Risk
Risk of business disruption which may be caused by hardware or software failure, cyberattacks, unauthorized access to company information, and the like, or lost opportunities associated with lack of innovation or investments in technology.

People Risk
Refers to factors and events that could compromise the well-being, productivity, and performance of our employees.

Financial Risk
Refers to matters that could affect the financial position or performance of the Company such as credit, liquidity and foreign currency risks.

Legal and Compliance Risk
Includes risks related to compliance to rules and regulations, adaption to changing political landscapes and new government pronouncements, as well as exposures that could arise from contractual obligations, anti-competition and monopolization concerns, and legal disputes against the company.
Risk Response, Monitoring, and Reporting
For each priority risk, we develop appropriate risk responses that align with the Company's risk appetite and overall risk management strategy. At the enterprise level, we implement responses for risks that are common across the Group, fostering a cohesive and integrated approach to risk management.
Risk Owners are tasked to continually monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the risk responses. Material residual risks are regularly assessed to improve risk responses and identify recovery measures. Given the dynamic nature of risks, the entire risk management is an iterative process at the functional units of our operating companies and at the Group level. The risk management framework is presented to the AURROC for review on a regular basis, and the key risks are being updated and reported annually.
Building on our overarching ERM framework, the following outlines the risk management process adopted and applied to sustainability and climate-related matters.
Top Risks
To ensure that all relevant risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated, the Company’s risk register is reviewed periodically, considering changes in the Company’s business environment. Risks that are rated high are deliberated and calibrated by the Risk Council as they relate to the Company’s risk appetite and perceived vulnerabilities. The result of this assessment is reflected in the key risks for the year.
In 2024, we recognize cybersecurity, capital allocation and portfolio management, and volatility in interest and foreign exchange rates as the most impactful risks to the Company’s operational resilience, financial performance, and strategic priorities. Given their significance, we continuously enhance and implement targeted mitigation strategies to proactively manage these risks.

1. Cybersecurity
Loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information, data, or information systems resulting from a cyber attack or data breach
Implications
- Operational disruptions
- Loss of critical information
- Loss of credibility and erosion of brand value
- Sanctions and fines
Risk Drivers
- Increasing cyber threats in frequency and sophistication
- Vulnerabilities of vendors and third-party service providers
- Human error and gaps in employee awareness
- Deficiencies in incident response plans
Mitigation
- Robust vulnerability management, assessment, and testing
- Enhanced identity and access management
- Use of data encryption solutions
- Due diligence on outsourced partners
- Regular information security compliance audits
- Continuous monitoring and threat scanning
- Employee awareness and training programs

2. Capital Allocation / Portfolio Strategy
Overexposure to industries that are experiencing unfavorable trends, and missed opportunities in high-growth and profitable sectors due to potentially suboptimal capital allocation or investment decisions derived from assumptions that may not materialize
Implications
- Lower return on investments and financial losses
- Impaired or stranded assets
- Negative impact to long-term value creation
Risk Drivers
- Unfavorable macro-economic conditions and industry-specific trends
- Elevated debt levels and limited funding access
- Deviations of actual investment/divestment outcomes from assumptions
Mitigation
- Consistent monitoring of industry trends
- Regular review of investment and divestment opportunities and capital funding requirements
- Stringent investment/divestment evaluation and approval process
- Periodic review of the SBUs' strategic plan
3. Interest Rate / Forex Risk
Variability in the group's financial performance due to unpredictability of interest rates and/or forex rates
Implications
- Forex losses on foreign-denominated debts and transactions
- Increased debt service cost
- Reduced margins on imported goods and raw materials
Risk Drivers
- Central bank monetary policy changes
- High debt levels and an unfavorable mix of interest rate structures and maturities
- Forex fluctuation, depreciation of local currency
- Market volatility due to geopolitical events
Mitigation
- Borrowing in local currency to avoid forex risk on debt
- Investments in less risky fixed-income instruments
- Preparation of sensitivity analysis and regular reporting of exposure and potential impact on the bottom line
- Constant monitoring of macro factor movements
Risk Categories
Beyond the top risks, we recognize the broader risk landscape that could affect different aspects of our business. The following outlines our approach to managing risks under each risk category.
Legal and Compliance Risk

Regulatory changes pose a significant risk to the Company as failure to comply with evolving laws and industry standards could expose the Company to legal penalties, fines, and reputational damage. Non-compliance with regulations, including those related to tax laws, product safety, environmental protection, data privacy, and corporate governance, may lead to financial liabilities, operational disruptions, and erosion of stakeholder trust.
Considering that the Group operates in various industries across different jurisdictions, it is critical to establish strong controls that minimize non-compliance risks and ensure adherence to varied regulatory requirements. To mitigate these risks, we closely monitor legislative developments, including key policies related to transition to low-carbon operations and climate resilience. We are also committed to strict adherence to data privacy laws, recognizing the potential legal and reputational consequences of non-compliance. To ensure compliance, we conduct extensive employee training on data protection, regularly review contracts and policies, and assess corporate activities for regulatory alignment.
Our in-house legal experts work proactively with business units to assess regulatory impacts, implement necessary legal safeguards, and ensure adherence to compliance requirements. When needed, we engage third-party consultants to strengthen our legal position and provide specialized expertise. Additionally, we actively engage with regulators, industry bodies, and other stakeholders to stay ahead of regulatory developments and advocate for fair and balanced policies.
People Risk

On people risk, talent development and retention remain to be crucial in the face of intense competition for key talents, especially for those within the information technology and digital space. High attrition could result in business disruptions, compromised service quality, and increased cost of talent acquisition and training. We continually upgrade our talent acquisition strategies, conduct wages and benefits benchmarking, and employ data insights and advanced analytics in developing HR programs for employees’ professional growth and development to address these risks.
The Company values a diverse workforce, recognizing that different perspectives drive innovation and enhance our ability to serve a broad range of stakeholders. A culture of inclusivity strengthens our talent pipeline and helps unlock opportunities in untapped markets. We also foster a safe and open environment for employees to communicate their concerns with management. Maintaining constructive labor relations is essential in reaching mutually beneficial agreements, minimizing the risk of disputes that could escalate into unrest and operational disruptions.
We continue to highlight the importance of health and safety, not just in the workplace but everywhere else. We strive to ensure that employees are healthy and safe because we understand the consequences to life and property if this is not addressed properly. Noncompliance with health and safety standards and regulations could also cost the Company penalties from regulators, suspension of operations, attrition, and damage to reputation.
Climate Risk

JG Summit recognizes the significance of climate-related risks. A company’s inability to mitigate or address the impact of extreme weather events could result in damage to facilities, obsolescence or loss of assets, disruptions in its supply chain and operations, as well as endanger people and the ecosystem. Enhancing infrastructure resilience against extreme weather events and adapting to changing conditions could require significant financial and capital investments. Regulatory changes related to climate change, such as carbon pricing, emissions caps, and extended producer responsibility, may also affect the company’s operations and financial results due to escalating compliance costs.
To address these risks, we have encouraged the SBUs to conduct vulnerability assessments of critical facilities and implement risk management measures across operations and supply chains. Furthermore, we enabled the SBUs to assess and prioritize climate related regulatory and market risks and conduct scenario analyses to anticipate potential impacts. We are monitoring evolving carbon policies and sustainability regulations to ensure that the Group will be prepared to navigate compliance challenges while exploring opportunities for efficiencies and savings.
For a more comprehensive discussion of our approach to managing climate risks, please refer to pages 18–27 of our 2023 Sustainability Report.
Operational Risk

We take compromised product or service quality risks very seriously, as any failure in this area can lead to customer dissatisfaction, regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses. Maintaining high safety and quality standards is essential to preserving trust and ensuring business continuity. Closely linked to this is operational reliability and efficiency, as equipment failures, system disruptions, or inefficient processes can compromise product integrity and service delivery. To mitigate these risks, we enforce stringent quality controls, adhere to safety regulations, and invest in preventive maintenance and continuous process improvements to enhance operational resilience.
Material cost and availability present additional operational challenges, as fluctuating commodity prices, rising input costs, and material shortages can significantly impact production efficiency, profitability, and overall business continuity. Supply chain disruptions, whether driven by geopolitical factors, economic conditions, or logistical constraints, may further amplify these risks by limiting access to critical raw materials. To address these potential vulnerabilities, we diversify our sourcing strategies and maintain strong supplier accreditation processes to ensure a stable and sustainable supply of quality inputs.
Our Company also considers the long-term implications of resource consumption, beyond just reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By recognizing the potential for material scarcity, we are taking steps to reduce the Company’s reliance on nonrenewable materials and adopt sustainable sourcing practices. We also recognize the potential risks to human health and the environment, posed by air emissions, air pollutants, and solid waste, and we are taking steps to manage them responsibly. We are implementing measures to reduce these emissions, such as improving combustion efficiency or using low-emission fuels. Similarly, we adopt solid waste management practices, including recycling and better product designs to minimize waste generation, in order to reduce negative impacts on the environment and surrounding communities. We also address the potential for leakages in the waste management system through regular maintenance and monitoring.
Geohazards and man-made disasters pose another significant operational risk, with potential impacts on physical assets, business operations, and personnel safety. In response, we continuously assess site vulnerabilities and implement robust emergency response protocols. We also ensure that adequate insurance coverage is maintained to mitigate financial exposure, and that business continuity plans are in place to ensure swift recovery from disruptions.
Strategic Risk

Our strategic risk covers areas of capital allocation, business performance and competition. This relates to how our long-term portfolio investment decisions may yield lower-than-expected returns. Additionally, unfavorable industry trends, market volatilities, and geopolitical uncertainties can affect enterprise value and market capitalization. These factors may also create an unfavorable perception of our value creation efforts and limit our growth prospects.
To manage these risks, we conduct in-depth sector analysis aligned with customer trends, integrate risk management into our strategic planning process, regularly review capital allocation decisions, and assess their impact on our risk-return profile. We also ensure that we effectively communicate our business performance and sustainability initiatives to key stakeholders.
IT and Digitalization Risk

Cybersecurity risk remains the most relevant IT and digitalization risk for the Group. The consequences related to this risk include loss of information, disruptions in business operations, increased cost of added security or disaster recovery, and potential loss of credibility and damage to brand and company image. This risk could also lead to significant regulatory violations. Data breaches could compromise the Company’s sensitive or confidential information and even jeopardize individuals’ privacy and protection, in case of personal data leaks. We are actively mitigating this risk as we continue to strengthen our security posture with pragmatic and holistic solutions to proactively identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover, as well as improve our system and data access controls. Actual cybersecurity incidents and their impact are investigated, resolved, and reported to the business unit management and Data Privacy Officer in case of data security breaches.
Beyond cybersecurity, the Company may also face challenges related to the availability and scalability of technological resources, the capacity for digital transformation, and potential IT system failures. The effectiveness of digital initiatives depends on the integration of people, processes, and tools, as well as employees' ability to adapt to evolving technologies and new ways of working. A lack of agility in digital adoption could hinder operational efficiency and long-term growth. To address these challenges, the Group leverages its ecosystem, resources, and partnerships to drive key digitalization initiatives. We also conduct external benchmarking to ensure alignment with industry best practices, and strategic organizational planning to support the sustainability and continuity of digital transformation efforts.
Financial Risk

Our key financial risks are primarily related to changes in market variables and liquidity. In recent years, we have experienced fluctuations in interest rates, commodity prices, and foreign exchange rates, which significantly impacted our Group’s financials. This includes margin compression due to higher input costs, higher cost of debt, and lower returns from financial investments.
We maintain a well-diversified mix of foreign-denominated financial assets and local currency borrowings, utilizing risk-appropriate instruments to hedge against foreign exchange volatility. Furthermore, we conduct rigorous periodic cash requirement analysis to optimize our debt portfolio and proactively manage financial obligations. Additionally, we continue to strengthen our onshore and offshore banking relationships to enhance our financial flexibility, allowing us to effectively manage liquidity needs.
Reputational Risk

Our reputational risk pertains to how public sentiment and third-party ratings and views affect our corporate image and brands. Misinformation about JG Summit and its subsidiaries, as well as unfavorable public opinion, could impact the Company’s social license to operate. Furthermore, unresolved customer complaints—especially when amplified through digital platforms—can shape wider customer perceptions of our product and service quality. Issues related to product safety, customer privacy, and advertising, if left unaddressed, may lead to declining customer satisfaction, sales, and market share.
We actively monitor mainstream and social media, track our market positioning, and manage external reputation risks. We follow established protocols for obtaining a social license to operate, recognizing that strong public and community engagement is essential to our long-term success. Failing to properly address stakeholder concerns could lead to opposition that negatively affects our operations.
Governance Risk

Our governance risk relates to compliance with company policies, ethical business practices, and adequate top management oversight. Unintended or intentional breaches of policies and ethical standards may lead to operational inefficiencies, significant financial losses, loss of stakeholder trust, or reputational damage. Weak governance structures could also compromise our ability to equitably distribute economic value to the right stakeholders.
To mitigate these risks, we continuously strengthen our internal processes and controls through capability-building initiatives, self-assessment tools, and effective risk management methodologies. We reinforce good corporate governance by conducting regular training on the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability across all levels of the organization. Additionally, we have strict anti-bribery and anti-corruption policies in place that prohibit corrupt practices, and a whistleblowing mechanism that allows stakeholders to report any suspected corruption or ethical misconduct.
Emerging Risk

We recognize that emerging risks, particularly geopolitical uncertainties and the rapid advancement of generative AI, could have significant implications for our business operations and strategic direction.
Geopolitical risks, including the ongoing Russia-Ukraine and Middle East conflicts, US-China trade tensions, and territorial issues in the West Philippine Sea, pose business challenges such as supply chain disruptions, rising input costs, and raw material sourcing difficulties potentially hampering stability, growth, and profitability. To address these risks, we actively monitor global developments and incorporate geopolitical risk analysis into our market and transaction evaluations. We also strengthen our business continuity planning by integrating supply chain resilience as a key scenario and ensuring emergency response plans and proactive measures are in place at the SBU level.
The rise of generative AI presents both opportunities and risks. While AI can drive efficiencies and innovation, it also introduces concerns such as increased cybersecurity threats, misinformation, ethical considerations, and the need for workforce reskilling and upskilling. If not effectively leveraged, AI advancements could impact our competitive position. In response, we are enhancing our cybersecurity measures, implementing AI policies and governance frameworks, and conducting awareness campaigns to educate employees on AI-related risks. Additionally, we are investing in upskilling programs to equip our workforce with the necessary digital competencies, ensuring that we harness AI’s potential while mitigating associated risks.

