Enterprise Risk Management
JGSHI recognizes the vital role of sound enterprise risk management (ERM) practices in driving business growth, long-term sustainability, and value creation for stakeholders. In an increasingly volatile and complex global environment, the Company maintains a proactive and dynamic approach to risk management, continuously refining its framework and processes to stay responsive to emerging risks and opportunities.
The Company’s ERM risk management approach is anchored on the principles of the COSO ERM Framework, which connects strategy setting with governance and risk management to foster a strong, risk-aware culture across the organization. Sustainability and climate-related risks and opportunities have been integrated into the ERM framework, aligning risk strategies with long- term ESG considerations to ensure a holistic approach to managing key business risks. Risk management practices are embedded across all levels of the organization, supported by systems and processes that enable the timely identification, assessment, monitoring, and mitigation of risks.
The Board of Directors oversees the adoption and implementation of the Company’s risk management framework and ensures that it remains effective and relevant through periodic reviews. This framework supports the identification of enterprise-level and business unit risks and evaluates the effectiveness of mitigation strategies and internal controls. To further strengthen risk capabilities across the organization, JGSHI implements ongoing initiatives such as training for risk owners and custodians, knowledge-sharing sessions for employees, and regular engagement with risk leaders across the group. These efforts promote a strong first-line risk awareness and enhance the organization’s ability to respond to evolving risks and industry best practices.
Enterprise Risk Governance
Effective risk governance is fundamental to the Company’s ERM framework, ensuring a structured approach to identifying and managing key business risks. The governance structure provides clear lines of responsibility and accountability, guiding the Board and Management in overseeing risk exposures at both the business unit and enterprise levels. This includes the governance of sustainability-related and climate- related risks, reinforcing the Company’s commitment to integrating these important risks into its overall risk management approach.
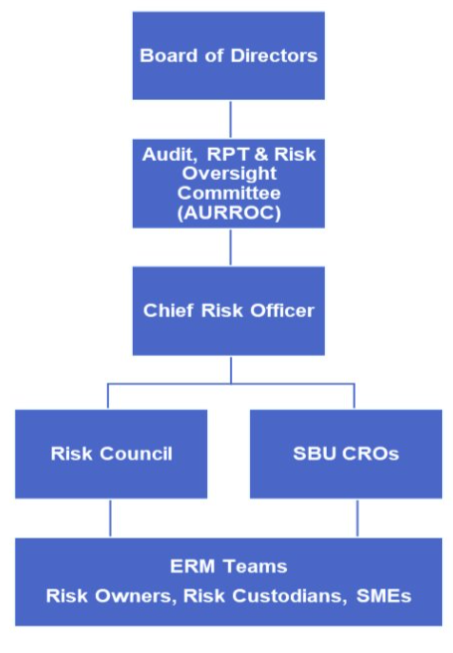
- The Board of Directors (BOD) provides oversight to JGSHI's risk management practices and sets guidelines in managing critical risks.
- The Audit, RPT and Risk Oversight Committee (AURROC) supports the BOD by monitoring the implementation of and assessing the effectiveness of the ERM framework.
- The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) holds ultimate accountability for the overall risk management approach of the company, ensuring that risk considerations are embedded in strategic decision-making and operations.
- The Chief Risk Officer (CRO) leads the development and implementation of the ERM framework and processes and is responsible for reporting risk exposures and mitigation efforts to Senior Management and AURROC.
- The Risk Council, composed of JGSHI functional heads, supports the CRO in identifying and addressing significant risk exposures and in overseeing the Company’s risk management strategies. Additionally, SBU CROs participate in Risk Council meetings to provide insights into the key risks affecting their respective business units, and support efforts to achieve a well-aligned and cohesive risk management approach across the Group.
- Risk Owners are accountable for the identification and management of risks in their assigned areas of responsibility, and communicating risk status and progress to the relevant stakeholders.
- Risk Custodians support the Risk Owners in the monitoring, analysis and reporting of risk status, trends, and progress of mitigation initiatives.
- The ERM Team supports the CRO in the development, continuous improvement and effective implementation of the ERM framework and methodologies across the organization.
- The Internal Control Team ensures that robust control mechanisms are in place to mitigate risks effectively, conducts periodic evaluations on the adequacy and effectiveness of controls and communicatessignificant control weaknesses or breaches to Management and AURROC.
- The Internal Audit Team provides independent assurance to Management and AURROC on the adequacy and effectiveness of the Company's risk management and internal control processes.
The Chief Finance and Risk Officer
The Chief Finance and Risk Officer (CFRO) leads the financial reporting, controllership and corporate forecasting functions guiding the Company to make sound business and financial decisions. He ensures a sound ERM framework is in place to effectively identify, monitor, assess, and manage key business risks, including sustainability and climate-related risks. He communicates significant risk exposures, control issues, and risk mitigation strategies to the AURROC. Under the risk and controls function, the CFRO is the steward of risk management, specifically those that have financial impact and affect company value.

RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
At the parent level, the Company provides guidance on the ERM framework to promote alignment in the risk management approach across the Group. It also fosters group-wide sharing of best practices and ERM learning initiatives. Each SBU establishes its own risk governance structure and processes to address the unique risks of its operations, according to its business environment, risk profile and strategic and operational goals.
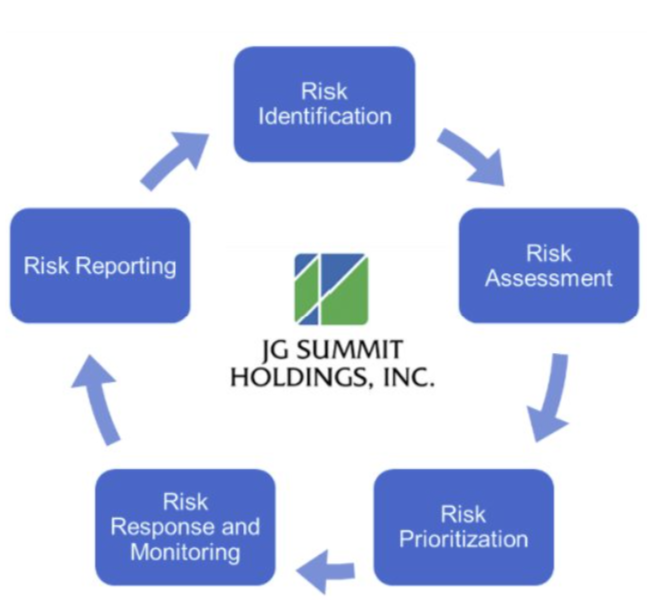
Risk Identification, Assessment, and Prioritization
Risks are identified using different tools such as risk factor analysis, megatrends analysis, and systems dynamics analysis. Identified risks are categorized and their potential impact is evaluated based on the risk assessment scale we developed for various impact areas. Likewise, likelihood parameters are set to define the probability of occurrence of the risks. Each operating company develops its own risk assessment scale according to their context and risk appetite.
Highly-rated risks undergo further evaluation to support prioritization, taking into account the organization’s overall risk profile, degree of vulnerability, and their potential to amplify other risks. The evaluation also considers the urgency of each risk, which is measured by its velocity, or how quickly the organization may feel its impact upon materialization, and the mitigation timeframe, or how long it would take to effectively manage the risk.
Risk Response, Monitoring, and Reporting
For each priority risk, the Company designs appropriate responses that are aligned with its risk appetite and overarching risk management strategy. Where risks are shared across the Group, coordinated responses are implemented at the enterprise level to promote a consistent and integrated approach to managing risk.
Risk Owners are tasked to continually monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the risk responses. Material residual risks are regularly assessed to improve risk responses and identify recovery measures. Given the dynamic nature of risks, the entire risk management is an iterative process at the functional units of our operating companies and at the Group level. The risk management framework is presented to the AURROC for review on a regular basis, and the key risks are being updated and reported annually.
The risk management process for sustainability and climate-related matters is outlined in the JGS Annual and Sustainability Report SEC Form (17A), Enterprise Risk Management, pp. 354-357.
TOP RISKS
To ensure that all relevant risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated, the Company’s risk register is reviewed periodically, considering changes in the Company’s business environment. Risks that are rated high are deliberated and calibrated by the Risk Council as they relate to the Company’s risk appetite and perceived vulnerabilities.
Details of the key risks identified through this process are available in the JGS Annual and Sustainability Report SEC Form (17A), Enterprise Risk Management, pp. 357-365.
IT Risk Governance
JGSHI recognizes that Cybersecurity controls are an essential component of any organization's overall security posture. The Company follows well known Cybersecurity frameworks such as National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The Company adheres to the following principles and best practices on security controls:
- A layered approach to security controls is used to protect the organization's assets. This includes physical security measures, such as access controls and surveillance cameras, as well as technical controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection software. The layered approach creates a more robust and effective security system.
- Regular testing and monitoring of security controls is conducted to ensure their effectiveness. This involves conducting penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and other types of security assessments to identify weaknesses in the security system. Regular monitoring of security logs and alerts also helps detect potential security incidents before they become serious threats. This process allows the Company to identify and address weaknesses in the security system, thereby reducing the risk of a successful cyberattack or data breach.
Effective management and reporting of identified security risks require a proactive and collaborative approach across the organization. JG Summit Information Security Office (JGS ISO) regularly reviews and updates risk management practices to adapt to the evolving threat landscape and changes within the organization.
To effectively manage and report identified cyber security risks, JGS ISO adheres to the following best practices:
- Prioritize identified security risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence and focuses on addressing high-priority risks first to mitigate the most significant threats to the conglomerate.
- Develop and implement risk mitigation strategies for each identified risk. Determine appropriate controls, safeguards, and countermeasures to reduce the likelihood and impact of the risks. Align these strategies with industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and to the organization's risk appetite.
- Information Security Incident Response Plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident related to the identified risks. Define roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and escalation procedures. Regularly test and update the plan to ensure its effectiveness.
- A continuous monitoring program to detect and respond to security incidents and changes in risk levels. Monitor security controls, conduct vulnerability assessments, and analyze security logs and alerts. Proactively identify and address emerging risks and vulnerabilities.
- Establishment of a robust reporting mechanism to communicate identified security risks to relevant stakeholders. Prepare clear and concise risk reports that provide an overview of the risks, their potential impact, and the status of risk mitigation efforts.
- Define clear and relevant metrics and KPIs to measure the effectiveness of your risk management efforts. Track and report on these metrics regularly to assess the progress in mitigating identified risks. This helps in demonstrating the organization's commitment to security and provides insights for continuous improvement.
- Conduct periodic risk reviews to reassess identified risks, evaluate the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies, and identify emerging risks. Incorporate feedback from security incidents, audits, and assessments into the risk management process. Use the findings to refine risk mitigation strategies and enhance security controls.
- Educate employees about the identified security risks, their potential impact, and their role in mitigating those risks. Provide regular training sessions and awareness programs to promote a culture of security within the organization. Encourage employees to report security incidents or potential risks promptly.

